Key Takeaways
-
Aquaponic systems combine fish farming with plant cultivation, creating a self-sustaining ecosystem.
-
Aeroponic systems grow plants with their roots suspended in the air and misted with nutrient solutions.
-
Both systems are highly water-efficient, making them ideal for areas with limited water resources.
-
Aquaponics uses natural fish waste as fertilizer, while aeroponics offers faster plant growth due to enhanced oxygenation.
-
Initial setup costs can vary, but both systems can be scaled for home or commercial use.
Introduction to Soilless Sustainable Agriculture
Soilless agriculture is transforming the way we think about farming. By eliminating the need for soil, we can grow plants in environments where traditional agriculture isn’t feasible. This method includes systems like aquaponics and aeroponics, both of which offer sustainable solutions for growing food. Let’s dive into these systems to understand their benefits and how you can start your own.
Understanding Aquaponic Systems
Aquaponics is an innovative farming method that combines aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics (growing plants in water). The fish produce waste, which is converted by bacteria into nutrients that the plants can absorb. This creates a closed-loop system where both plants and fish thrive.
“Aquaponics is a sustainable method of farming that uses fish waste to fertilize plants, creating a self-sustaining ecosystem.”
In an aquaponic system, the water from the fish tank is pumped to the plants. The plants absorb the nutrients and filter the water, which is then returned to the fish tank. This cycle continues, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and conserving water.
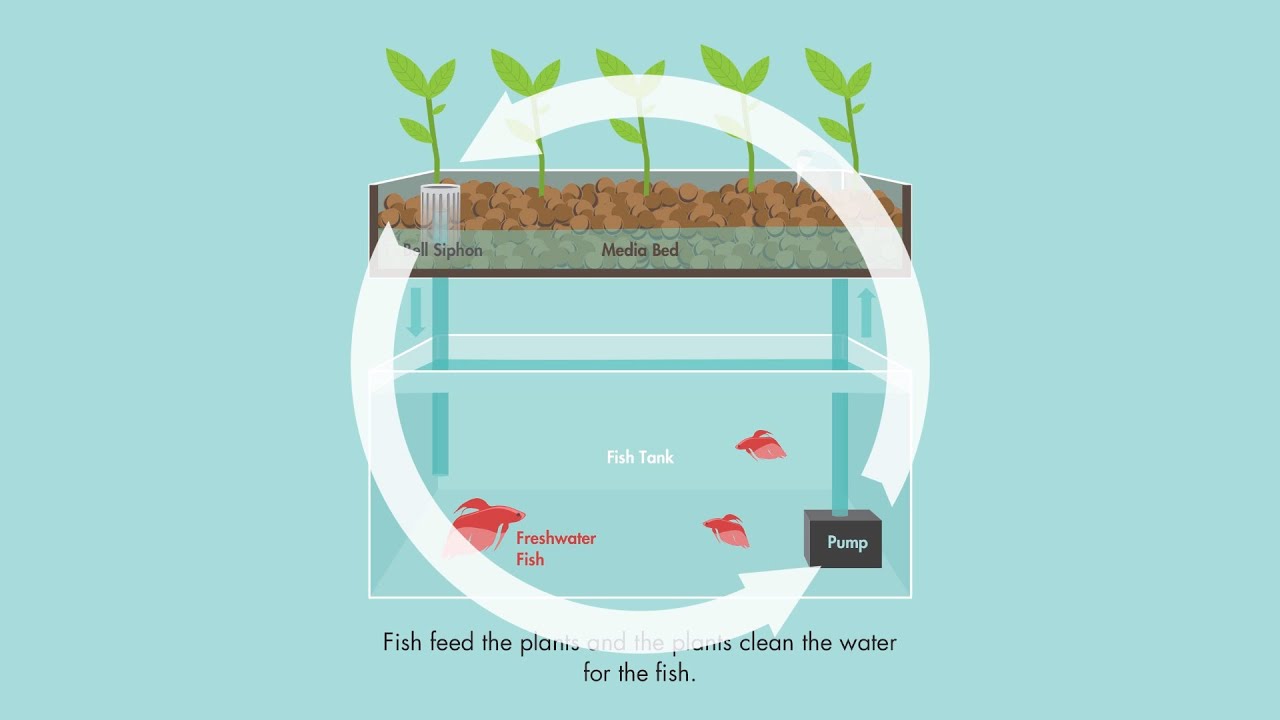
Types of Aquaponic Systems
For those interested in innovative farming techniques, exploring the different aquaponic systems can offer sustainable solutions for crop production.
There are several types of aquaponic systems, each with its own advantages. Understanding these types will help you choose the best system for your needs.
Media Bed
The media bed system is one of the simplest and most popular forms of aquaponics. It uses a grow bed filled with media like gravel or clay pellets to support the plants. Water from the fish tank is pumped into the grow bed, where it trickles through the media, providing nutrients to the plants.
This system is easy to set up and maintain, making it ideal for beginners. The media also provides a surface for beneficial bacteria to grow, which helps convert fish waste into nutrients for the plants. For more advanced projects, you can explore Arduino applications in aquaponic systems.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) involves a shallow stream of water containing dissolved nutrients flowing over the roots of plants. This system is efficient and uses less water than the media bed system. It’s particularly suited for growing leafy greens and herbs.
“NFT systems are highly efficient and use less water, making them perfect for growing leafy greens and herbs.”
In an NFT system, the plants are placed in channels with a thin film of nutrient-rich water flowing over their roots. The water is then recirculated back to the fish tank, ensuring minimal waste.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Deep Water Culture (DWC) is a popular hydroponic system where plant roots are suspended in a nutrient-rich, oxygenated water solution. This method allows for rapid growth and high yields, making it a favorite among hydroponic enthusiasts. For those looking to integrate technology into their systems, exploring smart greenhouse systems can provide valuable insights and solutions.
Deep Water Culture (DWC) is another popular aquaponic system. In this setup, plants are suspended in floating rafts with their roots submerged in nutrient-rich water. This system is ideal for growing larger plants like tomatoes and cucumbers. For more information on implementing smart systems in your greenhouse, check out smart greenhouse systems.
-
Plants are placed in floating rafts
-
Roots are submerged in nutrient-rich water
-
Ideal for larger plants like tomatoes and cucumbers
DWC systems provide excellent oxygenation to the roots, promoting faster growth. They are also relatively easy to set up and maintain, making them a great choice for both beginners and experienced growers.
Benefits of Aquaponic Systems
One of the main benefits of aquaponic systems is their ability to combine fish farming and plant cultivation in a sustainable way. For those interested in further exploring sustainable agriculture, you might want to learn about the Ultimate Guide to Aeroponics vs. Hydroponics for a comparison of different soilless farming techniques.
Aquaponic systems offer numerous benefits, making them an attractive option for sustainable agriculture. Let’s explore some of these advantages.
Water Efficiency
One of the most significant benefits of aquaponic systems is their water efficiency. These systems use up to 90% less water than traditional soil-based agriculture. The water is recirculated, reducing the need for constant irrigation and minimizing waste. For more insights on maintaining optimal conditions, check out these summer greenhouse maintenance tips.
Natural Fertilization
Aquaponics relies on natural fish waste to fertilize the plants. This eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers, making the system more environmentally friendly. The fish waste is converted by bacteria into nutrients that the plants can absorb, creating a natural and sustainable fertilization process.
Besides that, the plants help filter the water, providing a clean environment for the fish. This symbiotic relationship benefits both the plants and the fish, creating a balanced ecosystem.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Understanding the sustainability and environmental impact of modern farming techniques is crucial for future agricultural practices. For example, implementing smart greenhouse systems can significantly reduce resource consumption and promote eco-friendly farming methods.
Aquaponic systems are highly sustainable and have a minimal environmental impact. They reduce the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, which can harm the environment. Additionally, these systems can be set up in urban areas, reducing the need for transportation and lowering carbon emissions.
Furthermore, aquaponics can be used to grow a wide variety of crops, from leafy greens to fruiting plants. This versatility makes it an excellent option for sustainable food production.
-
Reduces need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides
-
Can be set up in urban areas
-
Wide variety of crops can be grown
Exploring Aeroponic Systems
Aeroponics is another innovative method of soilless agriculture. In an aeroponic system, plants are grown with their roots suspended in the air and misted with a nutrient-rich solution. This method provides excellent aeration and nutrient absorption, resulting in faster plant growth and higher yields.
Basic Aeroponic Setup
A basic aeroponic setup includes a chamber where the plant roots are suspended, a misting system to deliver nutrients, and a reservoir to hold the nutrient solution. The misting system sprays a fine mist of nutrients onto the roots, providing them with everything they need to grow.
“Aeroponic systems provide excellent aeration and nutrient absorption, resulting in faster plant growth and higher yields.”
This setup is relatively easy to maintain and can be used to grow a variety of crops. The key is to ensure that the misting system is working correctly and that the nutrient solution is properly balanced.
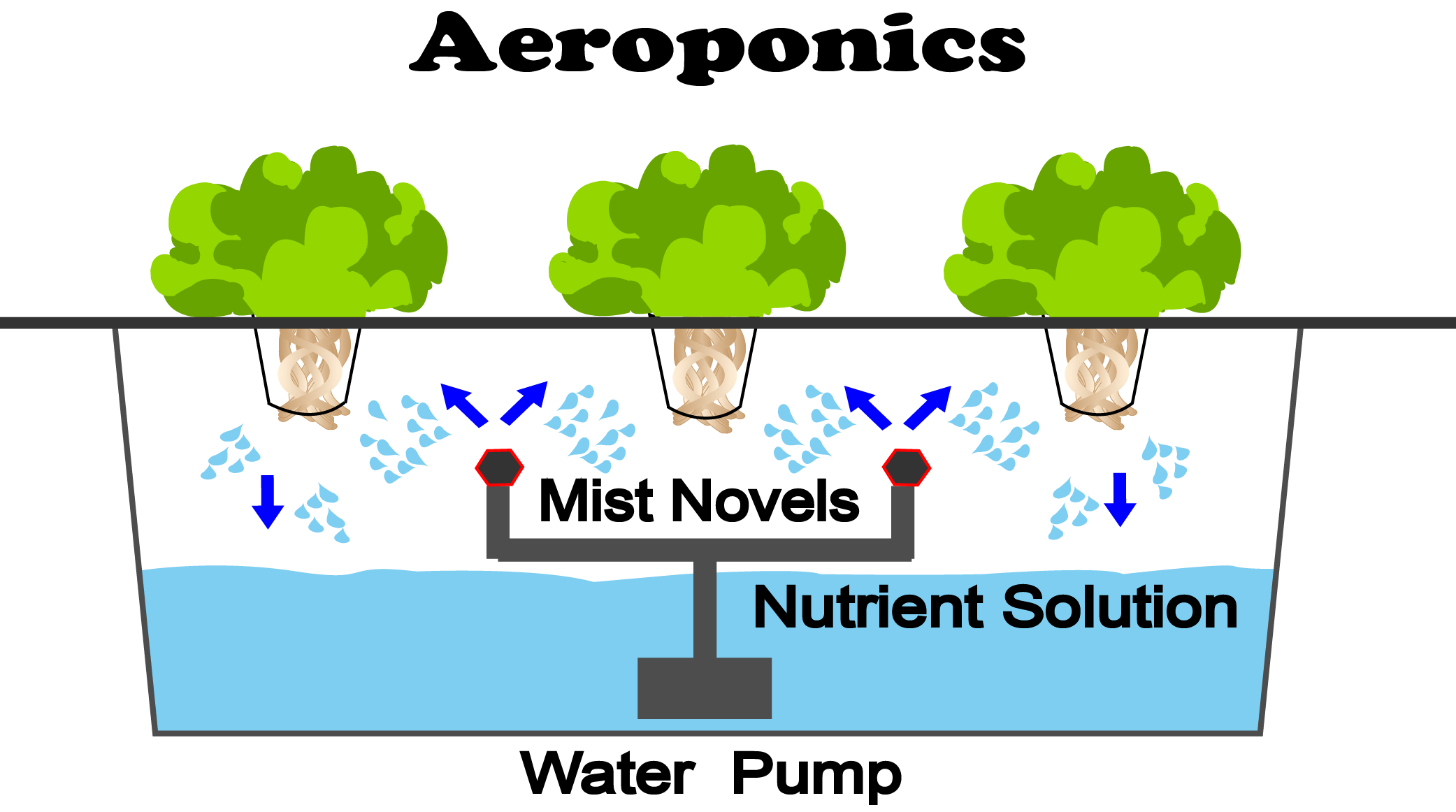
Types of Aeroponic Systems
There are two main types of aeroponic systems: high pressure and low pressure. Each type has its own advantages and is suited to different growing conditions.
High Pressure Aeroponics
High pressure aeroponics uses a high-pressure pump to create a fine mist of nutrients. This mist provides excellent coverage and ensures that the roots receive a consistent supply of nutrients. High pressure systems are ideal for commercial operations and can support larger plants. For more advanced projects, consider exploring Arduino applications in aeroponic systems.
These systems require specialized equipment and can be more expensive to set up. However, the increased efficiency and faster growth rates can offset the initial costs.
Low Pressure Aeroponics
Low pressure aeroponics uses a lower pressure pump to deliver a coarser mist of nutrients. These systems are simpler and less expensive to set up, making them ideal for home growers and small-scale operations.
While they may not provide the same level of nutrient coverage as high pressure systems, low pressure aeroponics can still produce excellent results. They are also easier to maintain and require less specialized equipment.
Benefits of Aeroponics
One of the major benefits of aeroponics is the efficient use of water and nutrients, which makes it a highly sustainable method of crop production. Additionally, aeroponics allows for faster plant growth and higher yields compared to traditional soil-based methods. For those interested in implementing this innovative technique, exploring best aquaponic and aeroponic systems can provide valuable insights and practical tips.
Aeroponic systems offer several advantages, making them a popular choice for sustainable agriculture. Let’s explore some of these benefits.
Water and Nutrient Efficiency
Aeroponic systems are highly efficient in their use of water and nutrients. The misting system ensures that the roots receive a consistent supply of nutrients, reducing waste and improving growth rates. This efficiency makes aeroponics an excellent option for areas with limited water resources. For further insights, check out this guide on smart greenhouse systems.
Faster Growth Cycles
Faster growth cycles in aquaponic and aeroponic systems are a key advantage for sustainable crop production. For those interested in the latest trends, check out the 2024 greenhouse gardening trends to watch.
One of the most significant benefits of aeroponics is the faster growth cycles. The increased oxygenation and nutrient absorption result in quicker plant growth and higher yields. This can be particularly advantageous for commercial growers looking to maximize their production.
Enhanced Oxygenation
The roots in an aeroponic system are exposed to more oxygen, which promotes healthier and faster growth. This enhanced oxygenation can lead to stronger plants and higher yields, making aeroponics a highly effective method of soilless agriculture. For more tips on optimizing your growing environment, check out this summer greenhouse maintenance guide.
Now that we have a good understanding of aquaponic and aeroponic systems, let’s explore the types of crops that are best suited for these methods.
Crops Best Suited for Aquaponic and Aeroponic Systems
Both aquaponic and aeroponic systems are versatile and can support a wide variety of crops. However, certain plants thrive better in each system due to their unique growing conditions. Let’s explore the crops best suited for these innovative farming methods.
Leafy Greens
Growing leafy greens can be incredibly rewarding, especially when utilizing innovative systems like aquaponics and aeroponics. For more information on these methods, check out this guide on best aquaponic and aeroponic projects.
Leafy greens like lettuce, spinach, and kale are excellent choices for both aquaponic and aeroponic systems. These plants have relatively shallow root systems and grow quickly, making them ideal for soilless agriculture. They benefit from the nutrient-rich water in aquaponics and the enhanced oxygenation in aeroponics.
For instance, in an aquaponic setup, leafy greens can help filter the water for the fish while thriving on the nutrients provided. In aeroponics, the fine mist ensures that their roots receive ample oxygen, promoting faster growth and higher yields.
Tomatoes
Tomatoes are another popular crop for soilless systems. They require more space and support, but both aquaponic and aeroponic systems can accommodate them with the right setup. Tomatoes benefit from the consistent nutrient supply and oxygenation, resulting in robust plants and bountiful harvests.
In aquaponics, tomatoes can be grown using trellises or other support structures to keep the plants upright. Aeroponic systems, with their superior oxygenation, can lead to faster fruiting and larger yields. For more information on advanced techniques, check out this guide on smart greenhouse systems.
Herbs
Herbs like basil, mint, and cilantro thrive in both aquaponic and aeroponic systems. These plants are relatively easy to grow and can be harvested frequently, making them a great choice for home gardeners and commercial growers alike.
In aquaponics, herbs can be planted in media beds or floating rafts, absorbing nutrients from the fish waste. Aeroponic systems, with their fine mist, provide excellent conditions for herb growth, resulting in flavorful and aromatic plants.
Strawberries
Growing strawberries in a greenhouse can be highly rewarding. To ensure your plants thrive, consider these summer greenhouse maintenance tips for hot weather care.
Strawberries are well-suited for both aquaponic and aeroponic systems. They require careful attention to nutrient levels and support, but the results can be highly rewarding. Strawberries grown in soilless systems often have better flavor and higher yields compared to traditional soil-grown strawberries.
“Strawberries grown in aquaponic and aeroponic systems often have better flavor and higher yields compared to traditional soil-grown strawberries.”
In aquaponics, strawberries can be grown in vertical towers or media beds, utilizing the nutrient-rich water. Aeroponic systems, with their enhanced oxygenation, can lead to faster growth and sweeter fruits.
Potatoes
For those interested in growing potatoes, consider checking out this guide to growing plants in a greenhouse to enhance your cultivation techniques.
Potatoes can also be grown in soilless systems, although they require more space and specific conditions. In aquaponics, potatoes are typically grown in media beds, where they can develop their tubers in the substrate. Aeroponic systems can also support potato growth, with the roots and tubers suspended in the air and misted with nutrients.
While growing potatoes in soilless systems can be more challenging, the results can be highly rewarding, with clean and disease-free tubers. For more insights, you can explore the Ultimate Guide to Aeroponics vs. Hydroponics.
Practical Considerations
When planning a sustainable crop production system, it’s essential to consider the implementation challenges and solutions associated with smart greenhouse systems. These systems can greatly enhance efficiency and productivity but require careful planning and management.
When deciding between aquaponic and aeroponic systems, it’s essential to consider practical factors such as initial setup costs, maintenance, and monitoring requirements. These considerations will help you choose the best system for your needs and ensure successful crop production.
Initial Setup Costs
Setting up an aquaponic or aeroponic system can be expensive initially. However, with proper planning and research, you can find the best DIY projects and systems to minimize costs and maximize efficiency.
Setting up an aquaponic or aeroponic system can involve significant initial costs. Aquaponic systems typically require tanks for the fish, grow beds, pumps, and plumbing. The cost can range from $500 to $5,000 or more, depending on the size and complexity of the system.

Aeroponic systems, on the other hand, require specialized misting equipment, pumps, and nutrient reservoirs. The initial cost for a basic aeroponic system can range from $300 to $2,000, with more advanced systems costing significantly more. For more information on advanced systems, check out these best aquaponic and aeroponic projects.

Maintenance and Monitoring
Both aquaponic and aeroponic systems require regular maintenance and monitoring to ensure optimal plant growth. In aquaponics, you need to monitor water quality, fish health, and nutrient levels. Regular cleaning of the tanks and grow beds is also necessary to prevent the buildup of waste and algae.
Aeroponic systems require careful monitoring of the misting system to ensure that the roots receive consistent nutrient coverage. The nutrient solution needs to be regularly replenished and balanced to prevent deficiencies or toxicities. Additionally, the misting nozzles should be cleaned to prevent clogging.
-
Monitor water quality and nutrient levels
-
Regular cleaning of tanks and grow beds
-
Ensure consistent misting and nutrient coverage
-
Replenish and balance nutrient solution
Considering these practical aspects will help you choose the best system for your needs and ensure successful crop production.
Comparison Between Aquaponic and Aeroponic Systems
Understanding the differences between aquaponic and aeroponic systems will help you make an informed decision about which method is best for your needs. Let’s compare these systems in terms of cost, infrastructure, ease of use, and scalability.
Cost and Infrastructure
Aquaponic systems generally require more infrastructure, including tanks for fish, grow beds, and plumbing. The initial setup cost can be higher, but the system can be more self-sustaining once established. Aeroponic systems, while potentially less expensive initially, require specialized misting equipment and regular maintenance to ensure consistent nutrient delivery.
Ease of Use
Both systems have their own challenges and learning curves. Aquaponic systems require knowledge of both fish farming and plant cultivation, while aeroponic systems demand careful attention to nutrient balance and misting schedules. However, with proper setup and maintenance, both systems can be highly productive and rewarding. For those interested in exploring innovative projects, check out these Arduino applications for aquaponic and aeroponic systems.
Scalability
When considering the scalability of modern agricultural systems, it is essential to explore innovative solutions such as aquaponic and aeroponic systems that can adapt to various scales of production.
Scalability is another important consideration. Aquaponic systems can be scaled up to support larger operations, but this requires more space and resources. Aeroponic systems, on the other hand, can be more easily scaled for vertical farming, making them ideal for urban environments with limited space.
In the next section, we’ll explore the steps to start your own aquaponic or aeroponic system, providing you with practical guidance to embark on your sustainable agriculture journey.
Steps to Start Your Own Aquaponic or Aeroponic System
Starting your own aquaponic or aeroponic system can be a rewarding endeavor. Here are the steps to get you started:
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
First, decide which system is best for you. Consider factors like space, budget, and the types of crops you want to grow. Aquaponic systems are great for those who want to integrate fish farming with plant cultivation, while aeroponic systems are ideal for maximizing plant growth and efficiency.
Gathering Necessary Supplies
Once you’ve chosen your system, gather the necessary supplies. For aquaponics, you’ll need fish tanks, grow beds, pumps, and plumbing. For aeroponics, you’ll need a misting system, nutrient reservoir, and grow chamber.
-
Fish tanks and grow beds (for aquaponics)
-
Misting system and nutrient reservoir (for aeroponics)
-
Pumps and plumbing
-
pH and nutrient testing kits
-
Seeds or seedlings
Setting Up and Testing Your System
For those interested in sustainable crop production, exploring the differences between aeroponics and hydroponics can be a great starting point. Understanding these systems can help in setting up and testing your own system effectively.
Set up your system according to the manufacturer’s instructions or your design plan. Ensure that all components are securely in place and that the system is functioning correctly. Test the water quality, nutrient levels, and misting system to ensure everything is balanced and ready for plants and fish.
Monitoring and Maintenance Tips
Regular monitoring and maintenance are essential for the success of your system. Check the water quality and nutrient levels weekly, and make adjustments as needed. Clean the tanks, grow beds, and misting nozzles regularly to prevent buildup and ensure optimal performance.
-
Monitor water quality and nutrient levels weekly
-
Clean tanks, grow beds, and misting nozzles regularly
-
Ensure consistent nutrient delivery and oxygenation
-
Adjust pH and nutrient levels as needed
For more detailed advice, check out our summer greenhouse maintenance tips.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both aquaponic and aeroponic systems offer innovative and sustainable solutions for crop production. By understanding the benefits and challenges of each system, you can choose the best method for your needs and embark on a rewarding journey in sustainable agriculture.
Final Thoughts on Sustainable Crop Production
Sustainable crop production through aquaponics and aeroponics is not only environmentally friendly but also highly efficient. These systems allow you to grow a variety of crops with minimal water and nutrient waste, making them ideal for urban environments and areas with limited resources. By starting your own system, you can contribute to a more sustainable future and enjoy fresh, home-grown produce year-round.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
For those interested in learning more about setting up a greenhouse, you can find detailed guidance in our greenhouse installation guide.
What is the difference between aquaponics and hydroponics?
Understanding the difference between aquaponics and hydroponics is crucial for anyone interested in sustainable farming. While both systems allow for soil-less plant growth, aquaponics integrates fish farming to create a symbiotic environment. For more insights on innovative farming techniques, check out these best aquaponic & aeroponic systems.
Aquaponics combines fish farming with plant cultivation, using fish waste to fertilize the plants. Hydroponics, on the other hand, involves growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution without the use of fish. Both methods are soilless and highly efficient, but aquaponics offers the added benefit of fish production. For more on innovative methods, explore best aquaponic & aeroponic projects.
How much does it cost to set up an aquaponic or aeroponic system?
The cost of setting up an aquaponic or aeroponic system can vary widely. A basic aquaponic system can range from $500 to $5,000 or more, depending on the size and complexity. Aeroponic systems can range from $300 to $2,000 for basic setups, with more advanced systems costing significantly more. It’s essential to consider your budget and goals when planning your system. For more information, check out these best aquaponic & aeroponic projects.
What are the most common challenges of using these systems?
Sustainable crop production methods like aquaponics and aeroponics are gaining popularity due to their efficiency and environmental benefits. These systems allow for the cultivation of plants without soil, using nutrient-rich water or mist to deliver essential nutrients directly to the roots.
For those interested in starting their own project, understanding how to start a community greenhouse project can provide valuable insights and resources to get started.
