Key Takeaways
- Vertical farming involves growing crops in stacked layers, often in urban settings, using minimal space.
- This method uses less water than traditional farming, typically reducing water usage by up to 95%.
- Three main techniques are employed: hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics, each with unique benefits.
- Vertical farms can operate year-round, providing fresh produce irrespective of weather conditions.
- Initial setup costs can be high, but long-term savings in water, space, and labor make it economically viable.
Welcome to the fascinating world of vertical farming, where agriculture meets innovation to create a sustainable future. If you’re curious about how we can grow more food with fewer resources, you’re in the right place. Vertical farming is not just a trend, it’s a revolution in how we think about food production.
Introduction to the World of Vertical Farming
Imagine growing lettuce in a skyscraper or tomatoes in a warehouse. That’s vertical farming. It’s an innovative approach to agriculture that maximizes space and resources to produce food in a controlled environment. This method allows us to grow crops in places you wouldn’t normally expect, like urban areas where land is scarce.
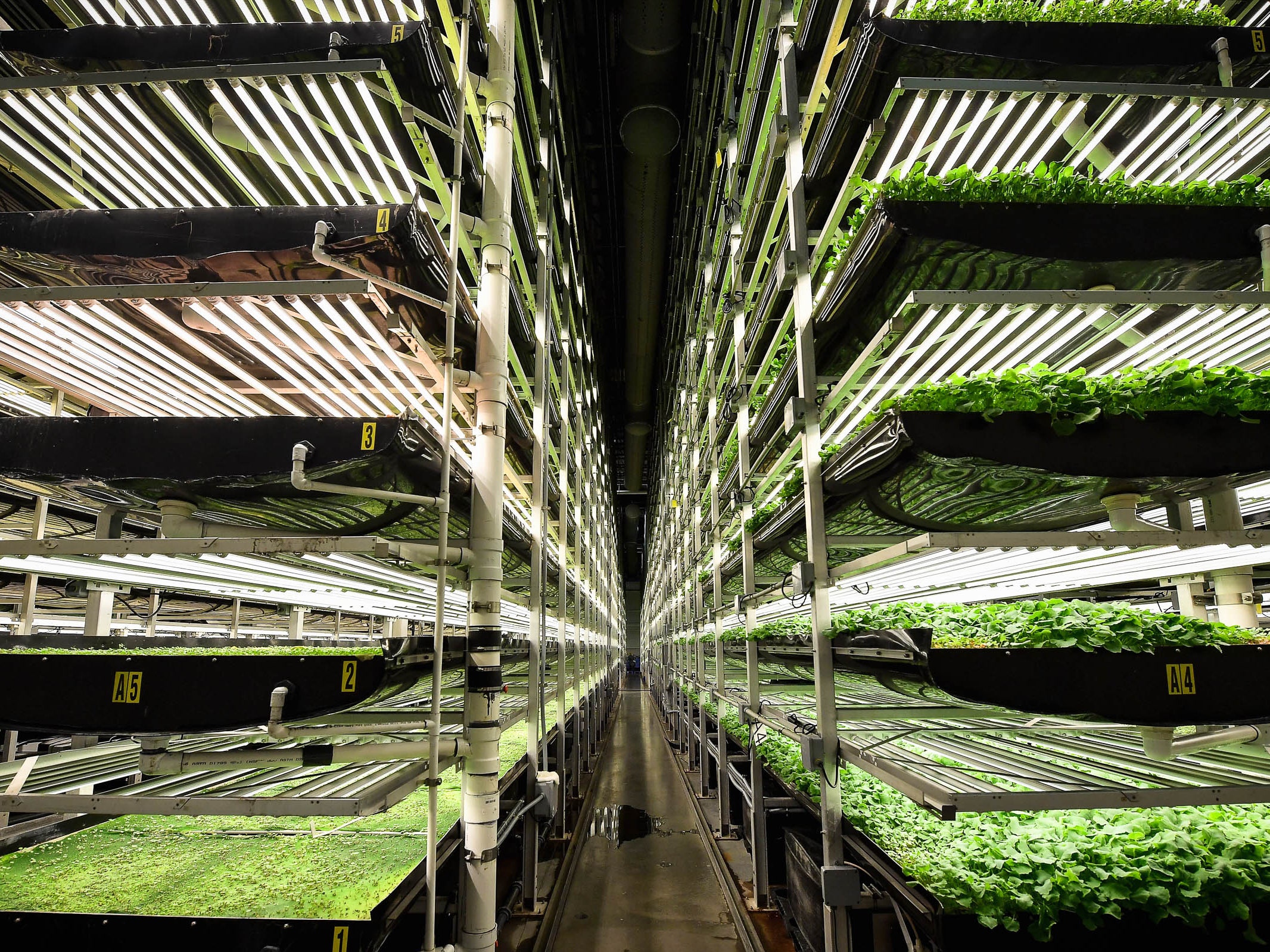

“Vertical Farming Has Found Its Fatal …” from www.wired.com.
Innovative Approach to Agriculture
Vertical farming represents a shift from traditional agricultural practices. Instead of spreading out over large tracts of land, crops are grown in vertically stacked layers. This approach is not only space-efficient but also allows for greater control over environmental conditions.
- Utilizes indoor farming techniques to control temperature, humidity, and light.
- Reduces the need for pesticides and herbicides, promoting healthier produce.
- Enables farming in urban environments, reducing food miles and carbon footprint.
Most importantly, vertical farming can help address food security issues by allowing cities to produce their own food supply. This can significantly reduce the reliance on rural farms and the transportation of goods over long distances. To learn more, check out this vertical farming guide.
Why Vertical Farming is Gaining Popularity
There are several compelling reasons why vertical farming is catching on worldwide. Firstly, it offers a solution to the challenge of feeding a growing global population. With urban areas expanding, there’s less land available for traditional farming. Vertical farming, therefore, provides a viable alternative.
Moreover, climate change is making weather patterns more unpredictable, which can devastate traditional crops. Vertical farms, however, operate in controlled environments, shielding them from adverse weather conditions. This ensures a consistent and reliable food supply, regardless of what’s happening outside.
Basics of Vertical Farming
To truly appreciate the potential of vertical farming, we need to understand its core concepts and structure. At its heart, vertical farming is about growing plants in vertically stacked layers, often in a closed, controlled environment. This setup allows for the precise management of light, temperature, humidity, and nutrients.
But how did this innovative method come about? Let’s delve into its historical development and evolution.
Core Concept and Structure
The concept of vertical farming isn’t entirely new. The idea of growing plants indoors dates back centuries, but modern vertical farming combines this with cutting-edge technology to maximize efficiency and yield. The typical structure of a vertical farm includes racks or towers where plants are grown using various techniques like hydroponics, aeroponics, or aquaponics.
Historical Development and Evolution
Vertical farming as we know it began gaining traction in the late 20th century, with advances in technology playing a pivotal role. The development of energy-efficient LED lights, for example, has made it feasible to grow plants indoors without relying on natural sunlight. Over the years, as urbanization has increased, so has the interest in vertical farming as a solution to space constraints and food security challenges.
Now, let’s explore how vertical farming operates and the technologies that make it possible.
How Vertical Farming Operates
Vertical farming is a sophisticated system that combines technology and agriculture to create optimal growing conditions for plants. These farms are typically housed in urban buildings, utilizing vertical space that would otherwise go unused. But what makes these environments so special? Discover the benefits and advantages of urban hydroponic farming to understand how these systems revolutionize modern agriculture.
Indoor Controlled Environments
One of the key features of vertical farming is its indoor controlled environment. This allows farmers to manipulate conditions to suit the needs of the plants, ensuring they receive the right amount of light, nutrients, and water. Because these environments are sealed off from the outside world, they are also protected from pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical treatments.
Key Technologies and Setup
Several technologies are integral to the success of vertical farming. For instance, LED lighting provides the specific wavelengths of light that plants need for photosynthesis, while climate control systems regulate temperature and humidity. Nutrient delivery systems, such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics, provide plants with the essential nutrients they need to thrive.

These systems work together to create a highly efficient growing environment, allowing plants to grow faster and produce higher yields than they would in traditional settings.
Cultivation Methods: Aeroponics, Hydroponics, and Aquaponics
Vertical farming employs various cultivation methods to optimize plant growth. Each method has its own set of advantages and is chosen based on the specific needs of the crops being grown.
Aeroponics involves growing plants in an air or mist environment without the use of soil. Nutrients are delivered to the plant roots via a nutrient-rich mist. This method is highly efficient in terms of water usage and allows for faster growth rates due to the increased oxygen exposure to the roots.
Hydroponics is a technique where plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution. The roots are submerged in this solution, which provides all the essential nutrients directly. Hydroponics allows for precise control over nutrient levels and is particularly effective in maximizing plant growth and yield.
Aquaponics combines hydroponics with aquaculture, where fish and plants are grown together in a symbiotic environment. The waste produced by the fish provides nutrients for the plants, and in turn, the plants help to filter and clean the water for the fish. This method promotes a sustainable ecosystem, reducing waste and conserving resources. To learn more about sustainable farming methods, check out this guide on vertical farming.
Benefits of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming offers numerous benefits over traditional farming methods, making it an attractive option for sustainable agriculture.
Environmental Impact Reduction
One of the most significant advantages of vertical farming is its ability to reduce environmental impact. Traditional farming often involves deforestation and land degradation, but vertical farming minimizes land use by growing crops upwards. Additionally, the controlled environment reduces the need for pesticides and herbicides, leading to cleaner produce and less chemical runoff.
Space-Efficiency and Urban Integration
Vertical farming is exceptionally space-efficient. By utilizing vertical space, these farms can produce a large amount of food in a small footprint. This makes them ideal for urban areas where land is limited and expensive. Urban integration of vertical farms can help cities become more self-sufficient in food production. For those interested in learning more about sustainable agriculture practices, consider exploring agriculture analytics in smart greenhouses.
Furthermore, vertical farms can be established in repurposed buildings, such as warehouses and factories, breathing new life into otherwise unused structures. This not only contributes to urban renewal but also provides fresh produce closer to consumers, reducing transportation costs and emissions. For a comprehensive overview of vertical farming, check out Vertical Farming 101 by EcoWatch.
Economic Advantages and Year-Round Harvest
Vertical farming offers economic benefits by enabling year-round crop production. Unlike traditional farming, which is subject to seasonal changes, vertical farms operate in controlled environments, allowing for continuous harvests regardless of external weather conditions. This consistency can lead to more stable food prices and supply.
“Vertical farming allows us to grow fresh produce year-round, providing a reliable food source no matter the season.” – Urban Farming Advocate
Although the initial investment in vertical farming infrastructure can be substantial, the long-term savings in water, land, and labor make it a financially viable option. Additionally, the ability to grow high-value crops, such as leafy greens and herbs, can lead to higher profit margins for farmers.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its many benefits, vertical farming does come with its own set of challenges and limitations. Understanding these is crucial for anyone considering this innovative approach to agriculture.
Energy Consumption and Solutions
- High energy requirements for artificial lighting and climate control systems.
- Potential for increased carbon footprint if renewable energy sources are not used.
- Need for technological advancements to improve energy efficiency.
Energy consumption is one of the primary challenges facing vertical farming. The use of artificial lighting and climate control systems requires significant amounts of energy. However, advancements in energy-efficient LED lighting and renewable energy sources are helping to mitigate these concerns.
To address energy consumption, many vertical farms are incorporating solar panels or wind turbines to offset their energy needs. By integrating renewable energy sources, these farms can reduce their carbon footprint and operate more sustainably.
Financial Investment and Economic Viability
The financial investment required for vertical farming can be a barrier to entry for some. The cost of setting up a vertical farm includes purchasing equipment, installing infrastructure, and maintaining the controlled environment. These initial costs can be high, but they are often offset by long-term savings in water, land, and labor.
To ensure economic viability, it’s important for vertical farms to focus on growing high-value crops and optimizing their operations for maximum efficiency. Additionally, as technology advances and becomes more affordable, the costs associated with vertical farming are expected to decrease, making it more accessible to a wider range of farmers.
Future Prospects and Innovations
The future of vertical farming is bright, with ongoing research and innovations paving the way for even more efficient and sustainable practices.
Emerging Technologies and Research
Emerging technologies, such as automation and artificial intelligence, are playing a significant role in the evolution of vertical farming. Automation can help streamline operations, reduce labor costs, and improve efficiency. Meanwhile, AI can assist in monitoring plant health and optimizing growing conditions, leading to higher yields and better quality produce.
Research is also focused on developing new plant varieties that are better suited to vertical farming environments. These varieties may have faster growth rates, higher nutritional content, or greater resistance to diseases, further enhancing the benefits of vertical farming.
Role in Addressing Global Food Security
Vertical farming holds the potential to significantly contribute to global food security. As the world’s population continues to grow, traditional farming methods alone may not suffice to meet the increasing demand for food. Vertical farming offers a viable solution by enabling high-density food production in urban areas, where the majority of the population resides. By reducing the distance food travels from farm to table, vertical farming can minimize food waste and improve access to fresh produce, especially in food deserts and densely populated cities.
Final Thoughts on Vertical Farming
Vertical farming is not just a novel idea, it is a transformative approach to agriculture that addresses many of the challenges faced by traditional farming. Its ability to produce food in a sustainable and efficient manner makes it a critical component of future food systems. As technology advances and becomes more accessible, vertical farming will likely become an integral part of urban planning and development, providing fresh produce to communities worldwide.
Sustainability and Innovation in Agriculture
Sustainability is at the core of vertical farming, as it seeks to use fewer resources while producing more food. By integrating innovative technologies and practices, vertical farming minimizes environmental impact and promotes healthier ecosystems. This method of farming is a testament to human ingenuity and our ability to adapt to changing circumstances. For a deeper understanding, check out this guide on vertical farming.
As we continue to innovate, the integration of vertical farming with other sustainable practices, such as renewable energy and waste recycling, will further enhance its environmental benefits. This holistic approach to agriculture can help create a more resilient and sustainable food system for future generations.
Moving Towards a Greener Future
Vertical farming represents a step towards a greener future, where food production is efficient, sustainable, and accessible to all. By embracing this innovative approach, we can reduce our reliance on traditional farming methods that often contribute to deforestation, soil degradation, and water scarcity. Instead, vertical farming offers a path forward that prioritizes environmental stewardship and the well-being of communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
As vertical farming gains popularity, many people have questions about how it works and its potential benefits. Here, we address some of the most common inquiries.
What are the main types of vertical farming techniques?
Vertical farming primarily employs three techniques: hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics. Hydroponics involves growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution, aeroponics suspends plant roots in air and delivers nutrients through a mist, and aquaponics combines fish farming with hydroponics to create a symbiotic ecosystem.
How does vertical farming save water?
- Water is recirculated within the system, minimizing waste.
- Closed environments reduce evaporation and runoff.
- Precise nutrient delivery systems use only the necessary amount of water.
Vertical farming systems are designed to use water efficiently. Unlike traditional farming, where a significant portion of water is lost through evaporation and runoff, vertical farms recirculate water within the system. This closed-loop approach ensures that plants receive the necessary amount of water without excess waste.
Additionally, the controlled environment of vertical farms minimizes evaporation, further conserving water resources. This efficient use of water makes vertical farming an attractive option in regions facing water scarcity.
Can vertical farming be done at home?
Yes, vertical farming can be adapted for home use. With the increasing availability of small-scale vertical farming kits, individuals can grow their own fresh produce in limited spaces, such as balconies or indoor areas. These kits often include everything needed to start, from growing racks to nutrient solutions.
Home vertical farming allows individuals to enjoy fresh, homegrown produce year-round, regardless of weather conditions. It also provides an opportunity to learn about sustainable agriculture practices and contribute to reducing one’s carbon footprint.
What crops are best suited for vertical farming?
Vertical farming is particularly well-suited for growing leafy greens, herbs, and microgreens. These crops have short growth cycles and can thrive in controlled environments. Examples include lettuce, spinach, kale, basil, mint, and arugula. For those interested in setting up a similar system, a comprehensive hydroponics greenhouse system setup guide can be a valuable resource.
However, advancements in vertical farming technology are expanding the range of crops that can be successfully grown. Some vertical farms are experimenting with fruiting plants, such as strawberries and tomatoes, as well as root vegetables like carrots and radishes. The key is to choose crops that align with the specific conditions and capabilities of the vertical farming system.
